Uterine Fibroids Embolization
What is uterine fibroids embolization?
Uterine Fibroids Embolization began in Paris in 19995 by a multidisciplinary group of interventional radiologists and gynecologists who had experience in Uterine Embolization to control bleeding after birth.
They tried the same technique to treat electively women with fibroids who complained severely about uterine bleeding. In 1999 we started to implement the same technique in Portugal, being the first ones to do it.
We are the largest group in the country with the largest experience in uterine embolization, and we also have the biggest published casuistries to demonstrate uterine embolization safety and effectiveness for fibroids, and most recently to adenomyosis.
We publish the potential to get pregnant after this treatment on a global scale. It is a non-invasive treatment, guided by image and performed by interventional radiologists. It is performed under local anesthesia, with no need for a scalpel or surgical incision on the skin.
We only insert a small plastic tube (catheter) into an artery in the groin or wrist. The catheter is guided by image up to the uterus. We perform the embolization on the uterus, that is to say, the obstruction of arteries that nourish the fibroids.
It is a very simple, safe, and painless treatment, and it is done in 30-60 minutes. Patients come in in the morning and are discharged by the end of the day. They can return to their normal lives and go back to work after 3 to 5 days.
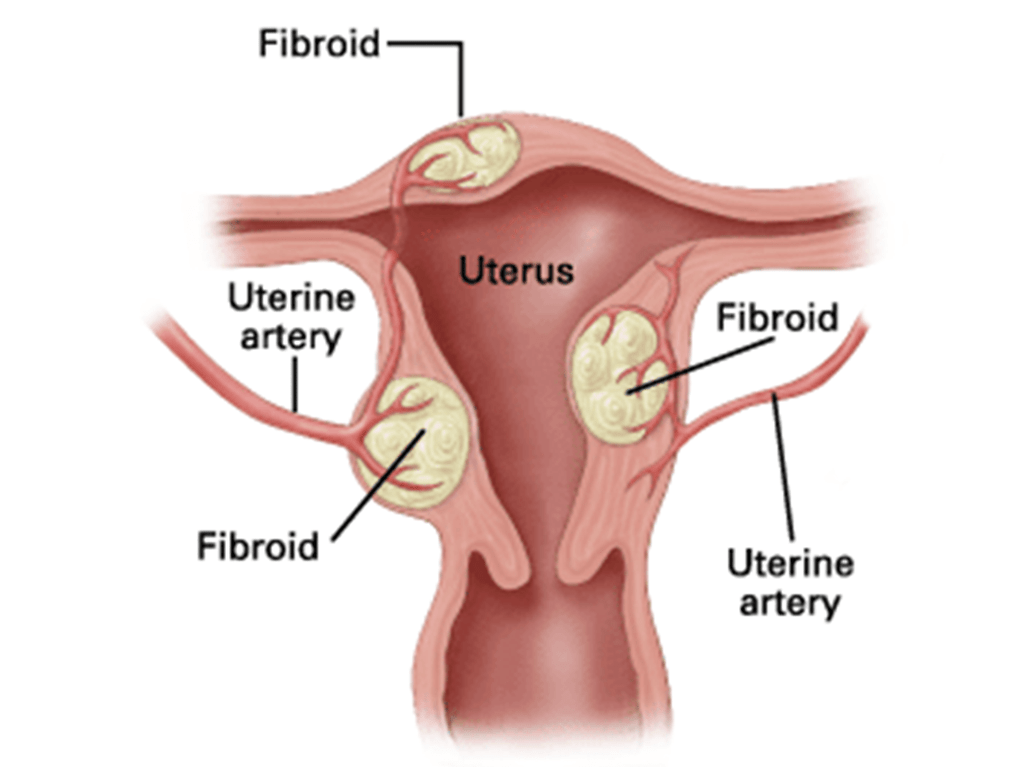
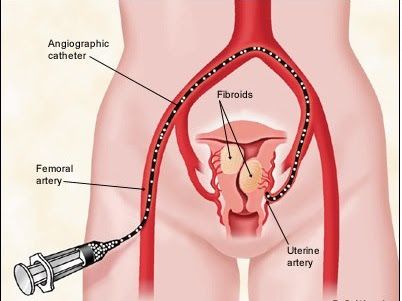




It is a very useful alternative to surgery because women have less pain and recovery is faster. The risks of serious complications are lower and the success rate in treating complaints is over 90%, close to the rate of surgery.
Besides, no incisions or cuts are made, there is no need for a scalpel, and we don’t have to “open” the abdomen to remove the uterus. There is no need for general anesthesia and there is no blood loss with this treatment.
Above all, with embolization women can preserve the uterus, being spared of more invasive treatments that can lead to more and worst complications.
This way, the embolization must be seriously considered for women who want to preserve their uterus or get pregnant, and which the only possible surgery is removing all the uterus (hysterectomy).
Despite all the advantages of uterine embolization regarding surgery, less than 7% of women with adenomyosis have access to it.
This is due to the fact of overall little information and dissemination of this technique and because, even inside the medical community, many women have no access to an interventional radiology appointment to evaluate the chances to be submitted to embolization rather than surgery.
How is the recovery after uterine embolization?
Most patients don’t feel any pain after embolization treatment. The recovery room is in a room next to the angiography room, where the embolization was performed.
If the vascular access to place the catheter is on the left wrist, at the end of the embolization you get a bracelet and you can walk freely in the room while you recover from the intervention.
If the vascular access is on the groin, a patch is placed, and you must remain in bed for 4 hours until you can start walking again. The patient recovers in a room for 4 hours. Usually, patients have no pain and can be discharged on the same day of the treatment.
Sometimes patients can feel some pain or nausea and vomiting after the embolization, that is why we prescribe medication. Usually, patients can’t eat immediately after uterine embolization.
Practically all patients are discharged on the same day of the procedure and can go home on their own. In the days following the embolization, there might be some pain and nausea that we control with prescribed medication.
What happens to adenomyosis after uterine embolization?
Most patients don’t feel any pain after embolization treatment. The recovery room is in a room next to the angiography room, where the embolization was performed.
If the vascular access to place the catheter is on the left wrist, at the end of the embolization you get a bracelet and you can walk freely in the room while you recover from the intervention.
If the vascular access is on the groin, a patch is placed, and you must remain in bed for 4 hours until you can start walking again. The patient recovers in a room for 4 hours. Usually, patients have no pain and can be discharged on the same day of the treatment.
Sometimes patients can feel some pain or nausea and vomiting after the embolization, that is why we prescribe medication. Usually, patients can’t eat immediately after uterine embolization.
Practically all patients are discharged on the same day of the procedure and can go home on their own. In the days following the embolization, there might be some pain and nausea that we control with prescribed medication.
What to expect after uterine embolization?
After the uterine embolization, the adenomyosis partially recedes its size. That is to say, the thickening of the junctional line detected on the MRI gets smaller. With that, the overall volume of the uterus also decreases.
Is uterine embolization painful?
No. Uterine embolization is minimally invasive, painless, or practically painless and it takes about 30 minutes to be done. The patient leaves the hospital on her own and the same day of the treatment. She can return home by car, train, or plane.
Some women tolerate uterine embolization so well that when they are in the recovery room it feels “like they went to the mall to buy socks”, as they are so comfortable/feel well.
However, there might be some pain complaints or nausea and vomiting hours after the embolization, that we control with prescribed medication.
Get in Touch.
Submit the form to schedule your appointment with Dr. Tiago.
Get in Touch.
Submit the form to schedule your appointment with Dr. Tiago.




